What is Pixel Density and Pixels Per Inch (Ppi)?

Have you ever wondered why some screens have a sharper display than others? You may have heard terms like ‘pixel density’ or ‘pixels per inch (PPI)’ but aren’t sure what they mean.
Well, fear not, because in this article, we’ll dive into pixel density and PPI to help you understand what they are and why they matter.
Pixel density refers to the number of pixels packed into a specific area of a screen. This can significantly impact the clarity and sharpness of images and text displayed on that screen.
Pixels per inch (PPI) is a measurement used to describe pixel density, indicating how many pixels are present within one inch of a screen. Understanding these concepts can help you make informed decisions when choosing devices with displays that meet your visual quality and clarity needs.
What is Pixel Density and Pixels Per Inch (Ppi)?
| Device | Pixel Density Range | PPI Range |
| Smartphone | 300-600 | 300-600 |
| Tablet | 200-400 | 200-400 |
| Laptop/PC | 100-200 | 100-200 |
| Monitor | 80-150 | 80-150 |
| TV | 40-100 | 40-100 |
Please note that the actual pixel density and PPI may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer of the device.
Imagine you’re trying to buy a new smartphone and wondering which one has the best display. You come across terms like pixel density and pixels per inch (PPI). What do they mean?
Simply put, pixel density refers to the number of pixels in a given area of a screen. PPI is the measurement used to determine pixel density. In other words, PPI tells you how many pixels are packed into every inch of your screen.
The higher the PPI, the more detailed and crisper images will appear. A high PPI means individual pixels are less visible, resulting in sharper visuals.
For instance, let’s say you’re comparing two smartphones: one with a 5-inch screen and 1080p resolution, while the other has a 6-inch screen with the exact resolution. Although both have the same number of pixels (1920×1080), the smaller phone would have a higher pixel density because it packs more pixels per inch into its smaller screen area.
Pixel Density & Viewing Distance
![]()
| Device | Pixel Density (PPI) | Recommended Viewing Distance |
| Smartphone | 300-600 | 12-18 inches (30-46 cm)a |
| Tablet | 200-400 | 18-24 inches (46-61 cm) |
| Laptop/PC Monitor | 100-200 | 24-36 inches (61-91 cm) |
| TV | 40-100 | 6-12 feet (1.8-3.7 meters) |
| Projector | 20-50 | 10-20 feet (3-6 meters) |
Please note that these are general recommendations and can vary depending on individual preferences and the specific display quality of the device or equipment.
Pixel density refers to the number of pixels packed into a given area, usually measured in pixels per inch (ppi). The higher the pixel density, the sharper and more detailed an image appears. A higher pixel density provides more information for each square inch of screen space.
However, pixel density becomes less critical when it comes to viewing distance. When viewed from a certain distance, all displays will eventually appear to have the same level of sharpness.
Therefore, you may not need an extremely high pixel density if you’re using a device mainly for reading or browsing websites from a typical viewing distance. That being said if you’re using your device for tasks such as photo editing or graphic design where fine details matter, a higher pixel density can make a significant difference in the quality of your work. Investing in a display with a high ppi resolution may be worth considering.
What is Ppi Resolution?
PPI, short for pixels per inch, is a measure of resolution commonly used in digital imagery. It refers to the number of pixels that can fit into one inch of space on a screen or print. The higher the PPI, the more detailed and clear the image will appear.
Pixel density is another related term for the number of pixels within a given area. It considers not only the image’s size but also its resolution. This means that two images with the exact pixel dimensions can have different pixel densities if their resolutions are different.
Understanding PPI and pixel density is crucial when creating high-quality graphics or printing materials. By knowing these terms, you can ensure that your images have enough detail and clarity to look great on any device or medium.
Why PPI matters:
– Higher PPI results in sharper and more detailed images.
– Low PPI can lead to blurry or pixelated images.
How to optimize your PPI:
– Determine the intended use of your image (e.g., web vs. print).
– Choose an appropriate resolution based on this use.
Now that we know what PPI is and why it’s essential, let’s dive into how to find the PPI of an image.
How to Find the Ppi of an Image.
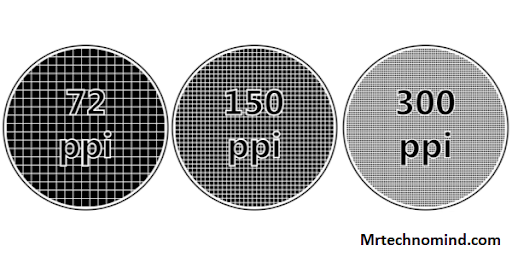
Have you ever wondered how to find the quality of an image? One way to do so is by measuring its pixel density or pixels per inch (ppi). Pixel density refers to the number of pixels present in one square inch of an image: the more pixels present, the higher the pixel density and, therefore, better image quality.
You need to know an image’s resolution and size to calculate the pixel density. The answer is measured in pixels on a horizontal and vertical axis, while the size is measured in inches. Using these values, you can determine the number of pixels per inch by dividing the total number of pixels by the whole area in square inches.
Take a look at this table below to see how different PPI values correlate with various types of displays:
| PPI | Display Type | Quality |
| <100 | Vintage CRT monitors | Poor |
| 100-200 | Budget laptops and tablets | Fair |
| 200-300 | High-end laptops and smartphones | Good |
| 300+ | Retina displays and professional-grade monitors | Excellent |
So now that we know how to find the PPI value for any given image or display, the question remains: How many pixels per inch do I need? This answer depends on your intended use of the image. A higher PPI value will generally result in a sharper and more detailed image. However, if you’re viewing a picture from far away or on a smaller screen, then a lower PPI value may suffice without sacrificing too much quality. Stay tuned for our next section, where we’ll dive deeper into this topic!
How Many Pixels Per Inch Do I Need?
![]()
| Use Case | Recommended PPI Range |
| Print Photography | 300 PPI or higher |
| Graphic Design | 250 PPI or higher |
| Reading Text | 200 PPI or higher |
| Gaming and Multimedia | 150 PPI or higher |
| Web Browsing and Videos | 100 PPI or higher |
| Basic Office Use | 80 PPI or higher |
| Casual Media Consumption | 60 PPI or higher |
When it comes to displaying resolution, pixel density and pixels per inch (ppi) are two terms that are often used interchangeably. But what do these terms mean?
Pixel density refers to the number of pixels that are packed into a given area of a screen. On the other hand, Pixels per inch measures how many individual pixels can be seen in one linear inch of a display.
So, how many pixels per inch do you need? The answer depends on what you plan to use your device for. If you primarily use your smartphone or tablet to read text-heavy content like e-books or articles, then you’ll want a higher pixel density and ppi. On the other hand, if you’re using your device mainly for streaming videos or playing games, then a lower pixel density might suffice.
Ultimately, the number of pixels per inch right for you will depend on your preferences and intended usage. However, with technological advancements and the increasing demand for high-quality displays across all devices, we can expect to see even higher pixel densities and ppi.
After all, who doesn’t love crisp and clear images?
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How Does Pixel Density Affect Battery Life on a Device?
Pixel density refers to the number of pixels packed into a particular space, usually measured in pixels per inch (ppi).
But did you know that pixel density can also impact your device’s battery life?
The more pixels there are on your screen, the harder your device has to work to display them all. This means that a higher pixel density can lead to shorter battery life.
However, advancements in technology have allowed for devices with high pixel densities to maintain still long battery lives through efficient power management techniques.
So if you value both high-resolution displays and long-lasting battery life, it’s essential to consider the balance between the two when choosing a device.
2. Can Pixel Density Be Increased on a Device After It Has Been Manufactured?
Imagine upgrading your device’s screen to have even crisper and more apparent visuals without purchasing a brand-new one.
While many may assume that pixel density is a feature that can only be determined during manufacturing, there are ways to increase it on a current device.
This process, known as pixel scaling, involves manipulating the current pixels on the screen to create more compact and defined images.
While it may not be a straightforward process, with the help of software updates or external devices, increasing pixel density is possible for those looking to take their viewing experience to the next level.
3. Are Any Drawbacks to Having a High Ppi Resolution on a Device?
Having a high PPI resolution on a device is every tech enthusiast’s dream come true! It means your favourite movies, games, and videos will display stunningly and sharply.
However, there are some drawbacks to having a high PPI resolution. Firstly, it can drain your battery faster as the device must work harder to process all those pixels. Additionally, not all apps and content are optimized for such high resolutions, which can lead to compatibility issues and distorted visuals.
Ultimately, while having a high PPI is impressive, it’s essential to consider other factors before making your final decision.
4. How Does Pixel Density Affect the Quality of Printed Images?
Pixel density is a crucial factor in determining the quality of printed images. The higher the pixel density, the more precise and detailed the picture appears when published. This is because pixel density refers to how many pixels are crammed into each inch of an image.
An image with a high pixel density means there are more pixels per inch (ppi), resulting in a sharper and more lifelike appearance. If you value high-quality prints with vibrant colours and intricate details, you should focus on finding devices with high pixel densities and ppi resolutions!
5. Is There a Difference in Pixel Density Between Lcd and Oled Screens?
Regarding screen technology, OLED is the clear winner regarding pixel density.
While both LCD and OLED screens use pixels to display images, OLED screens have a higher pixel density due to their unique design.
This means that images on an OLED screen appear sharper and more vibrant than those on an LCD screen.
With the ever-increasing demand for high-quality displays, it’s no wonder many tech companies are turning to OLED technology for their products.
So if you’re looking for the best possible visual experience, consider investing in a device with an OLED screen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pixel density and PPI are crucial when purchasing a device. A high PPI resolution may look great on paper, but it can have drawbacks such as decreased battery life and potential eye strain. Finding a balance that works for you and your needs is essential.
Simply put, buying a device is like picking out a pair of shoes. You want something that looks good and feels comfortable, but you also need to consider the practicality of wearing them daily.
Just as you wouldn’t choose shoes with too high heel or uncomfortable material, you should carefully consider the pixel density and PPI when selecting a device.
Finding the right balance between aesthetics and functionality will ultimately lead to a more satisfying experience overall.